資料威脅對世界各地造成了嚴重損害。從先前的文章中,我們可以得知這些資料威脅將在未來繼續增加。作為首席安全官或 IT 管理員,您不僅應該擔心病毒或惡意軟件的威脅,還應關注資料恢復的成本。實施全面的核心資料保護計劃可以保護您的公司免受資料威脅。
什麼是核心資料保護?
大多數的資料威脅來自外部網絡,通過強力入侵、DDoS 或魚叉式釣魚攻擊。這些威脅會針對核心資料或業務服務進行攻擊,以關閉運營並導致財務損失。
核心資料保護是資料安全三部曲中的第一道防線。這種保護的目的是防止任何資料威脅,防止惡意軟件和駭客入侵核心資料和業務服務。只有當滿足以下要求時,核心資料才能被視為完整保護:
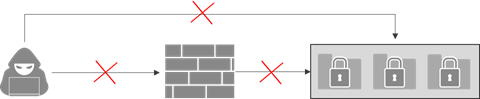
- 防止外部資料威脅 – 通過外部網絡保護方法來阻止惡意軟件和 DDoS,確保核心資料和業務的安全。
- 防止資料威脅攻擊核心資料 – 鎖定核心資料以防止惡意軟件或勒索軟件的任何刪除或修改。
- 防止核心資料被竊取 – 對核心資料進行加密,使駭客無法竊取任何重要資料。
實現核心資料保護
簡而言之,實現核心資料保護就是要阻止所有的資料威脅,確保服務不中斷,資料不會丟失。
隨著資料威脅的增加,資料安全的重要性也日益提升。企業需要通過儲存設備的安全功能建立一個深度防禦策略,實現最大程度的防禦協作能力,將資料威脅降至最低。
以下表格展示了不同儲存供應商提供的功能,以實現核心資料保護。
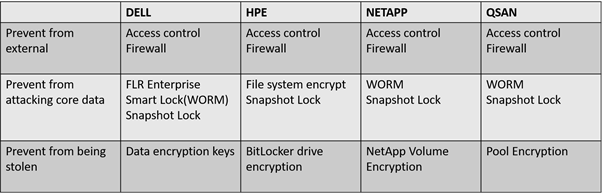
大多數供應商都有自己的核心資料保護方式。上述表格顯示,大多數供應商選擇 WORM(一寫多讀) 來保護他們的核心資料。WORM 可以防止核心資料被竄改或修改,為資料提供全面的保護。供應商關注的第二個功能是 Snapshot Lock(快照鎖定)。
儘管 Snapshot Lock 與 WORM 相似,但它用於保護核心資料的快照,以實現雙重保護。這兩個功能可以確保核心資料的全面保護,而且非常容易設置,因此它們是企業資料安全的首選。
當我們完成核心資料保護時,我們可以實現全面的保護。從外部連接到核心資料,我們可以使資料威脅變得無效。
如何應對資料威脅
自從開始這個部落格以來,我們一直專注於如何防止核心資料受到威脅。預防的主要目的,再次強調,是為了避免停機。然而,現實情況是,沒有 100% 的預防策略。如果發生資料威脅的情況 – 不要驚慌。在本系列的下一篇文章中,將重點討論三部曲的第二部分,我們將討論本地快速恢復,並向您展示如何快速從網絡攻擊中恢復過來。
遵循 QSAN 資料安全三部曲,您可以快速從攻擊中恢復,避免業務停機。
最好按照三部曲的順序閱讀並跟隨其中的內容:
- 二部曲 – 智能快速恢復可幫助您將RTO縮減到最低
- 三部曲 – 異地備份在您的本地系統受到攻擊時,仍然能夠保護您的服務
要了解有關勒索軟件 QSAN 資料安全三部曲的更多資訊,請參考以下資料:



