Since resources are limited, no matter budgetary or physical resources, storage solutions vendors are committed to improving data storage efficiency. On the other hand, software-defined data reduction policies are also the keys to the dilemma.
Data reduction is a general description of the technology of reducing the practical capacity of raw data. Deduplication and compression are the most common policies used to help organizations deal with the growing data. Therefore, we will look at both features and find out the advantages and possible disadvantages.
Compression
Data compression is a data storage technology designed to reduce the size of files or data sets. By encoding information more efficiently, compression minimizes the amount of space required to store the data without sacrificing its essential content.
In the enterprise, compression is widely used in a variety of applications to optimize storage, increase data transfer speeds, and improve overall storage efficiency. Backup and archive are the best applications for compression. Other data types that are accessed infrequently are also suitable for compression, such as file sharing or log file management.
Compression might be more commonly used for different types of applications in enterprises. Nonetheless, some disadvantages restrict compression efficiency. Firstly, compression efficiency is strongly related to the storage vendor’s algorithm and mechanism. In addition, there are some data types that limit the performance of compression. For example, encrypted data is too complex to compress. Frequently accessed data may also not be suitable for compression policy.
Deduplication
Data deduplication is a data compression technology designed to reduce redundant copies of data. Instead of storing multiple instances of the same data, deduplication identifies and eliminates duplicate blocks so that only one copy remains. This results in significant storage space savings without compromising data integrity.
Deduplication is usually used when your data acquires a large amount of redundant data that is repeated regularly. For example, a virtualized environment creates virtual machines repetitively. In most cases, IT members will create the same virtual machines, and the data diversity is only user information. In this case, deduplication may be the ideal solution.
Despite the benefits of deduplication technology, it also has some limitations. The throughput takes the brunt when enabling deduplication. Deduped data needs to be searched when the client access the data. Thus, powerful storage device is required. Secondly, deduplication only works if the entire data is mostly the same. When deploying deduplication, relying on traditional hard drives may cause indexing failures due to relatively slow read and write speeds. Deduplication processes involve intensive indexing and comparison of data chunks, and traditional hard drives may struggle to meet the performance demands, resulting in delays and potential failures during the indexing phase. Therefore, storage vendors tend do use all-flash array strategy to meet performance requirements.
Guidelines to Assist in Determining the Use of Data Reduction
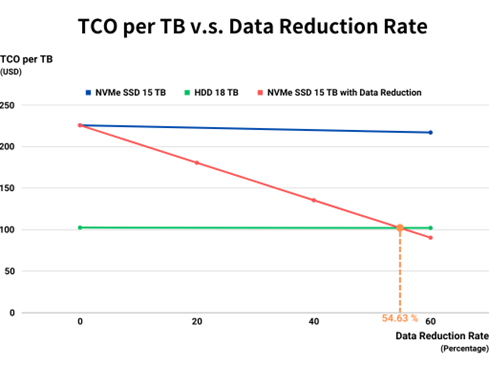
Although data reduction applications are limited, there are still more cost effective in most cases. According to the SNIA report, the TCO (Total Cost of Ownership) percentage per TB of “Traditional HDDs : NVMe SSDs” is approximately 45.37%. When the application data reduction rate reaches 54.63% or higher, the deduplication strategy will achieve better TCO than deploying a new storage device, as shown in the figure below. Since the application is more suitable for deduplication strategy, the better TCO can be accomplished. In addition, data reduction policies may result performance reduction, but the experience of deploying SSDs in a storage environment will still become more powerful.
Conclusion
Data compression emerges as a versatile storage technology that minimizes the space required to store data without affecting its essential content. It is widely used in a variety of enterprise applications to optimize storage, increase data transfer speeds, and facilitate backup and archiving. However, its efficiency depends on the storage vendor’s algorithm, and certain data types such as encrypted or frequently accessed data may pose challenges for optimal compression performance.
Deduplication is a technology that is good at eliminating redundant copies of data, stands out a valuable policy in scenarios where data repetition is prevalent, such as in virtualized environments.
While providing substantial storage capacity savings and cost efficiencies, there are also performance trade-offs. As a result, organizations must balance cost savings with potential performance overhead when designing their storage environment.



