In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, limited resources—whether budgetary or physical—present ongoing challenges for organizations. Storage solution vendors have responded by prioritizing data reduction technologies, enabling businesses to maximize storage efficiency and reduce costs.
Data reduction, a critical approach for managing growing data demands, encompasses key technologies such as deduplication and compression. This article explores how these methods can significantly enhance storage performance, alongside their advantages and challenges.
The Power of Compression
Data compression minimizes the size of files by encoding information more efficiently, reducing the storage space required while maintaining essential data integrity. This widely used technology optimizes enterprise storage, boosts data transfer speeds, and facilitates backups and archiving.
Compression is ideal for data types accessed infrequently, such as log files or shared files. However, its efficiency depends heavily on the storage vendor’s algorithm. For instance, encrypted or frequently accessed data can present compression challenges, as these types of data limit the performance gains compression provides.
Deduplication: Eliminating Redundancy
Data deduplication eliminates redundant data by retaining only one instance of repeated data blocks. This results in substantial space savings while maintaining data integrity. Deduplication is particularly effective in environments like virtualized systems, where repetitive data such as virtual machine copies are common.
Despite its advantages, deduplication demands robust storage devices, especially when indexing large data sets. The process can strain traditional HDDs due to their slower read and write speeds. To mitigate this, many storage vendors adopt all-flash array (AFA) strategies to meet performance requirements.
Choosing the Right Data Reduction Strategy
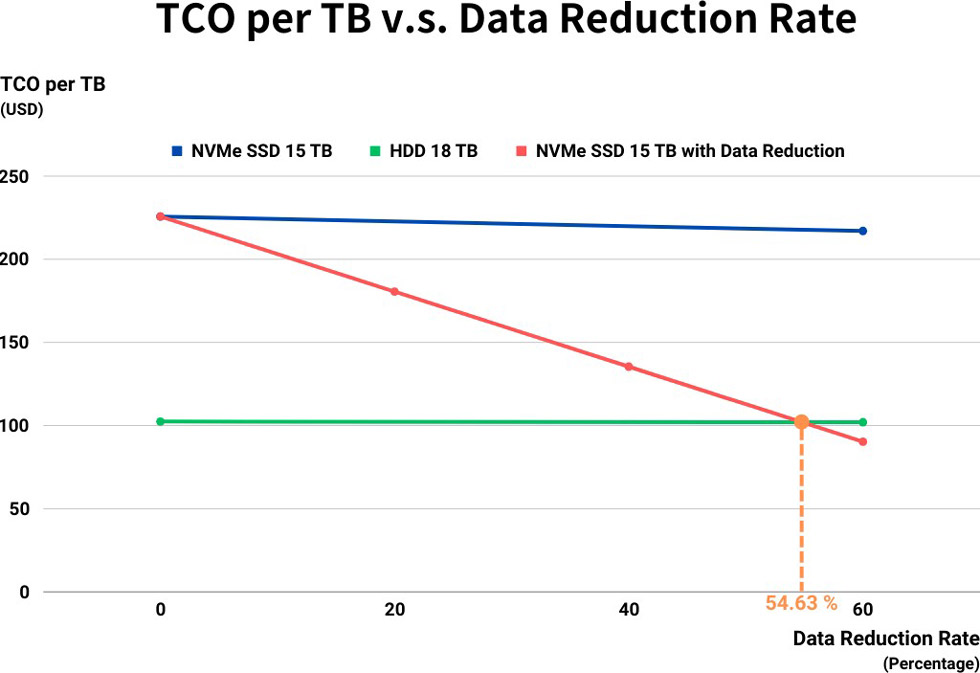
While both compression and deduplication have limitations, they remain cost-effective for most use cases. According to a SNIA report, the total cost of ownership (TCO) per terabyte for traditional HDDs versus NVMe SSDs is approximately 45.37%. When the data reduction rate exceeds 54.63%, deduplication strategies outperform deploying new devices in terms of TCO.
Organizations should evaluate their data types, access patterns, and storage infrastructure when adopting data reduction policies. While these strategies may slightly impact performance, incorporating SSDs into the storage environment can mitigate these issues and deliver enhanced efficiency.
Future Trends in Data Reduction Technology
Advanced data reduction technologies like compression and deduplication empower businesses to optimize storage, reduce costs, and tackle the challenges of data growth. While each method has its unique benefits and trade-offs, organizations must strike a balance between cost savings and performance. By leveraging modern storage solutions, such as QSAN’s NVMe-based systems, companies can overcome these challenges and achieve exceptional storage efficiency.



