A month after Broadcom acquired VMware in late 2023, perpetual licenses for VMware products have been taken away from its inventory. IT members of every organization are eager to seek alternatives to vSAN to eliminate as much possible overhead as possible. One of the significant issues is to deploy a physical SAN as one of the options. In this article, we’re going to discuss the pros and cons when configuring the IT environment.
What Exactly is vSAN?
Step 1
vSAN is an SDS (Software-Defined Storage) feature provided by vSphere developed by VMware. It is part of the vSphere virtualization product suite. vSAN integrates the local storage media (such as hard disk drives and solid state drives) from multiple physical hosts into a virtualized shared datastore, which can be managed and provisioned through VMware vCenter. VSAN has to provide storage resources for VMs (Virtual Machines) in a VMware environment.
Native Advantage of VMware Environment
Step 2
As a native suite of vSphere, vSAN provides the most compatible scenario in VMware VM environments. On the other hand, deploying vSAN in large-scale IT environments can easily reach many VMs through vSphere topology.
Is vSAN Sufficient for Your Application Needs?
Step 3
There are many advantages to a vSAN deployment, but some disadvantages cannot be ignored. Performance comes as the first consideration. vSAN is an SDS installed on an HCI (Hyper-Converged Infrastructure) or server. Data transfer speed slows down as it passes through a layer of software. According to the StorageReview article, this is the upper limit of performance and is far from HCI and typical SMB deployments, even in tests using the most powerful configurations. Additionally, the subscription policies might cause considerable overhead when configuring the IT structure with vSAN for the long term.
What You Get When Choosing a Physical SAN Array
Step 4
Some topics can be discussed when deploying a physical SAN as the storage solution.
Comprehensive Data Protection Helps
Physical SAN provides higher IOPS and throughput than the vSAN solution. Since vSphere has canceled the VDP (Data Protection) function starting from version 6.5, the data protection problem for VM backup is popping out. Physical SANs often offer useful backup features such as volume cloning or remote replication.
A Disadvantage in Physical SAN Adapted Environments
Moreover, physical SAN is at a disadvantage compared to the vSAN topology. When the virtualization environment reaches a certain scale, storage deployment might be more complex when the scale is too large to allocate the storage configurations. When encountering this scenario, the advantages of vSAN native SDS will be very obvious.
Comparison of vSAN and physical SAN
Below is a comparison table of vSAN and physical SAN.
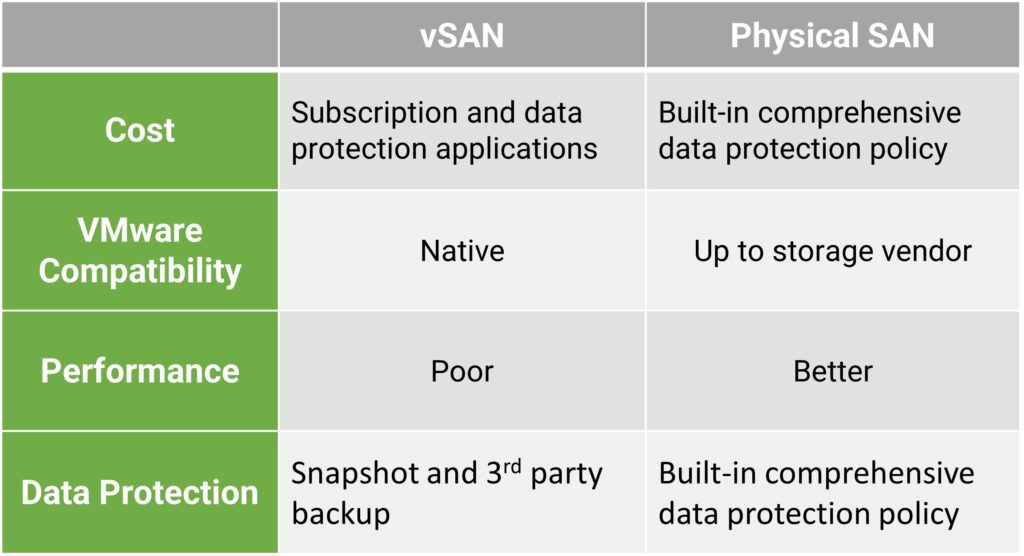
Choose vSAN or Physical SAN?
In summary, vSAN offers seamless integration, scalability, and compatibility benefits with VMware environments, but may suffer from performance overhead and long-term subscription costs. Physical SANs, on the other hand, offer higher performance and better data protection features but can be more complex to deploy and face larger scalability challenges. The choose between the two depends on your organization’s specific needs, considering factors such as performance requirements, scalability, compatibility, and long-term cost.



